
Flowering plants and pollinators, like bees, birds, and butterflies, depend on each other. Pollinators visit flowers to collect nectar and pollen for food. As they move from flower to flower, pollen, and thus genetic material, is dispersed among plants. So, the more attractive a flower is to a pollinator, the greater its chance for reproduction.
Flowers have many unique traits to advertise "Good Food Here!" and attract pollinators. Special versions of traits appeal to different pollinators.

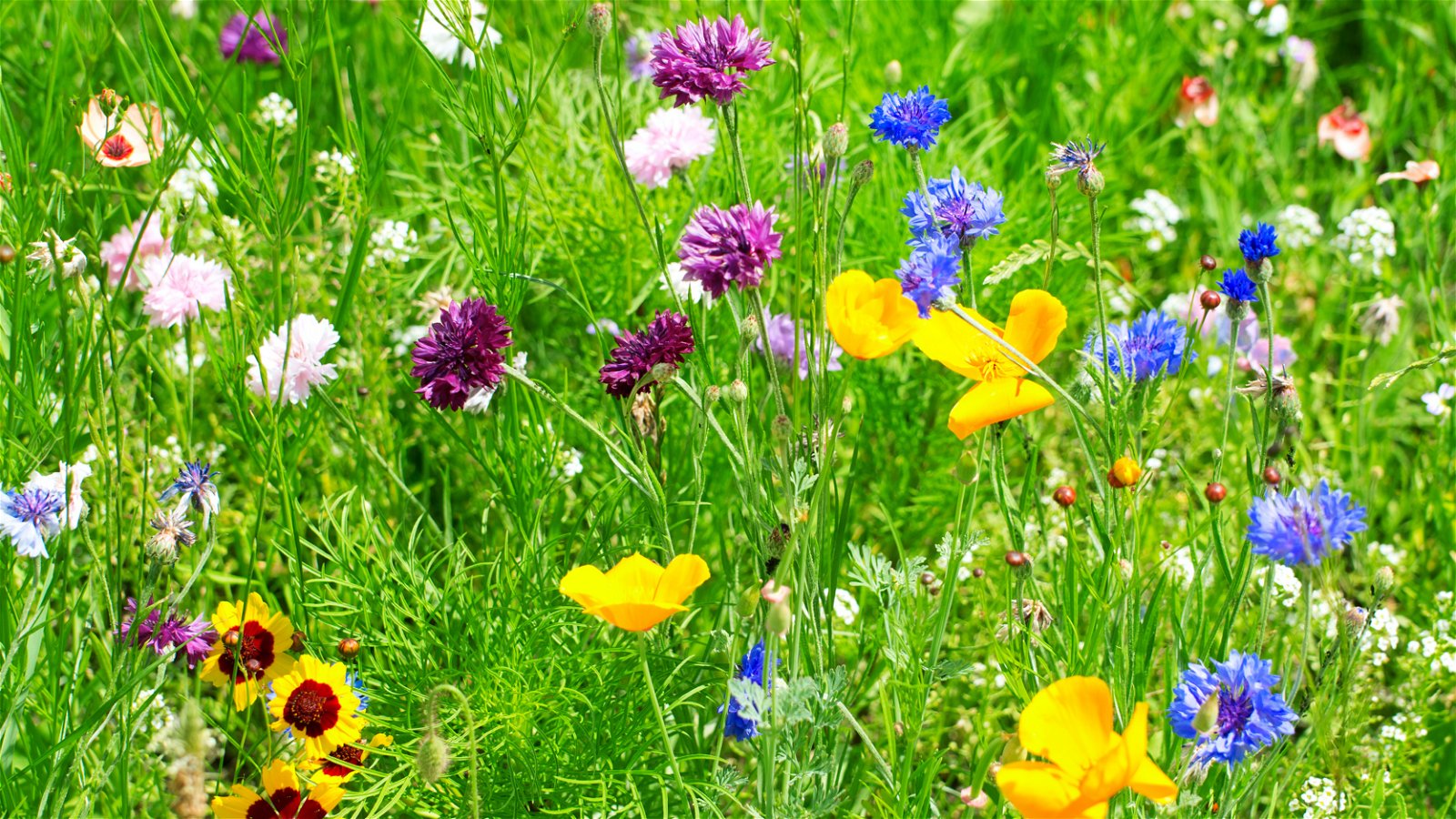
Color
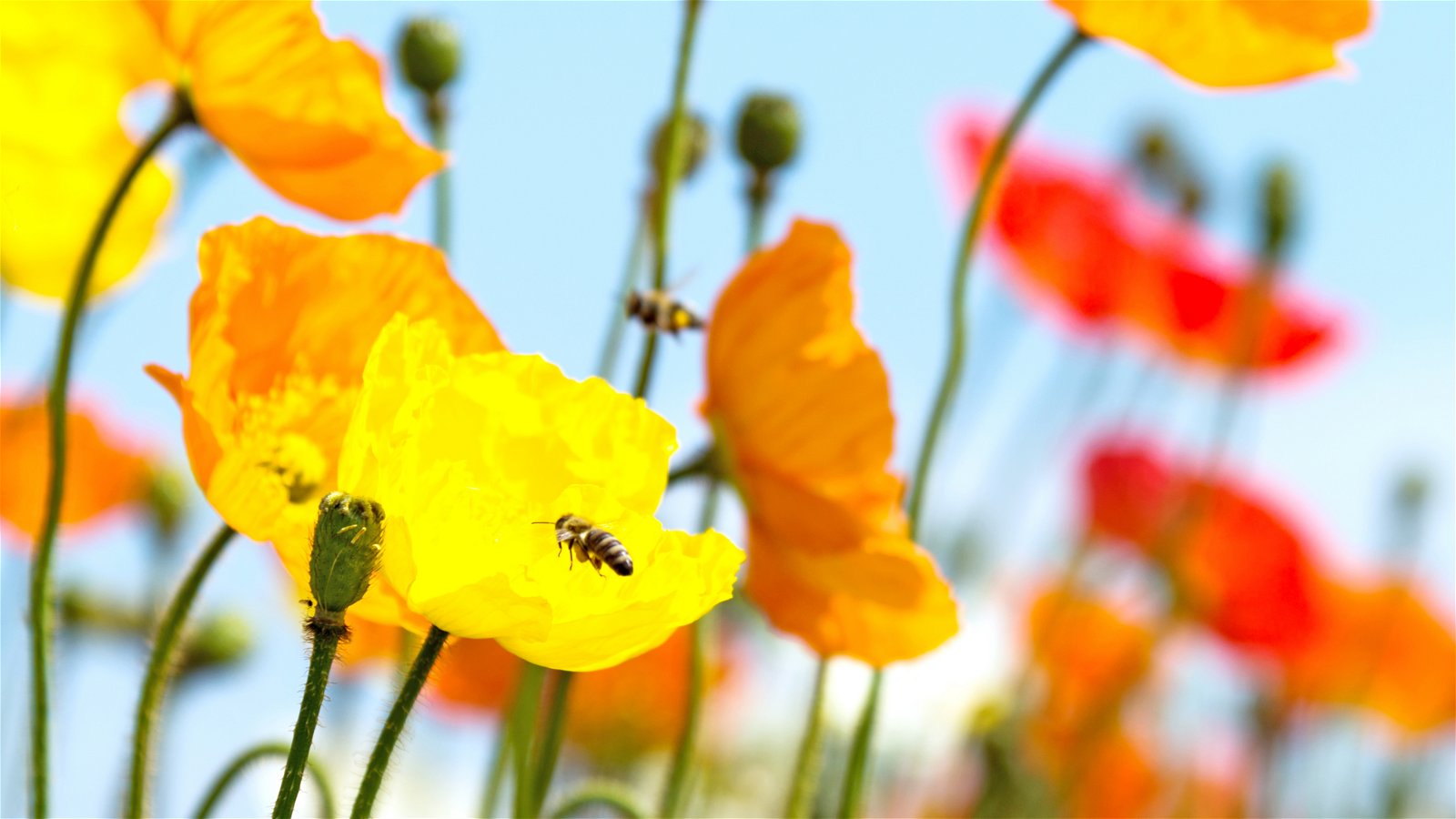
Bees are attracted to flowers with bright colors, especially blue and yellow. But bees can't see red, so a red flower isn't likely to catch their attention.
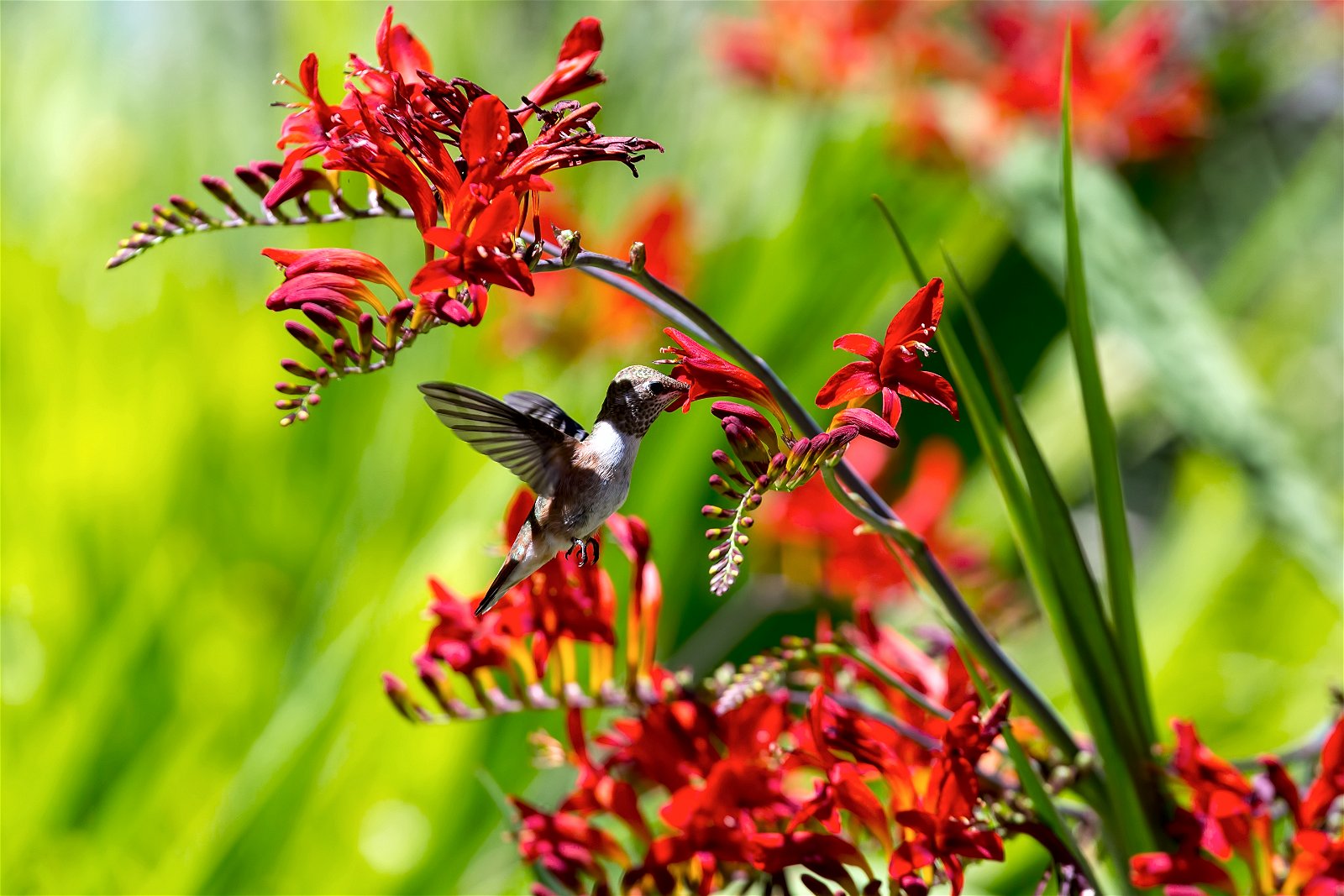

Color
Hummingbirds on the other hand, do see red. They pollinate the bright red flowers that bees overlook.

Pattern
The petals of some flowers have intricate patterns, called nectar guides, that direct pollinators straight to where the food is stored. Pollinators can find their meal quickly, then move on to the next flower.

Pattern
Two yellow stripes form the nectar guides of the monkeyflower species Mimulus lewisii. The color contrast directs bees to the pollen and nectar within the flower.
Without the visual cue from the nectar guides, bees get confused. They visit flowers less frequently. And, when they do visit, the bees often land upside-down! A disoriented bee is less likely to touch the correct parts of the flower to ensure pollination.
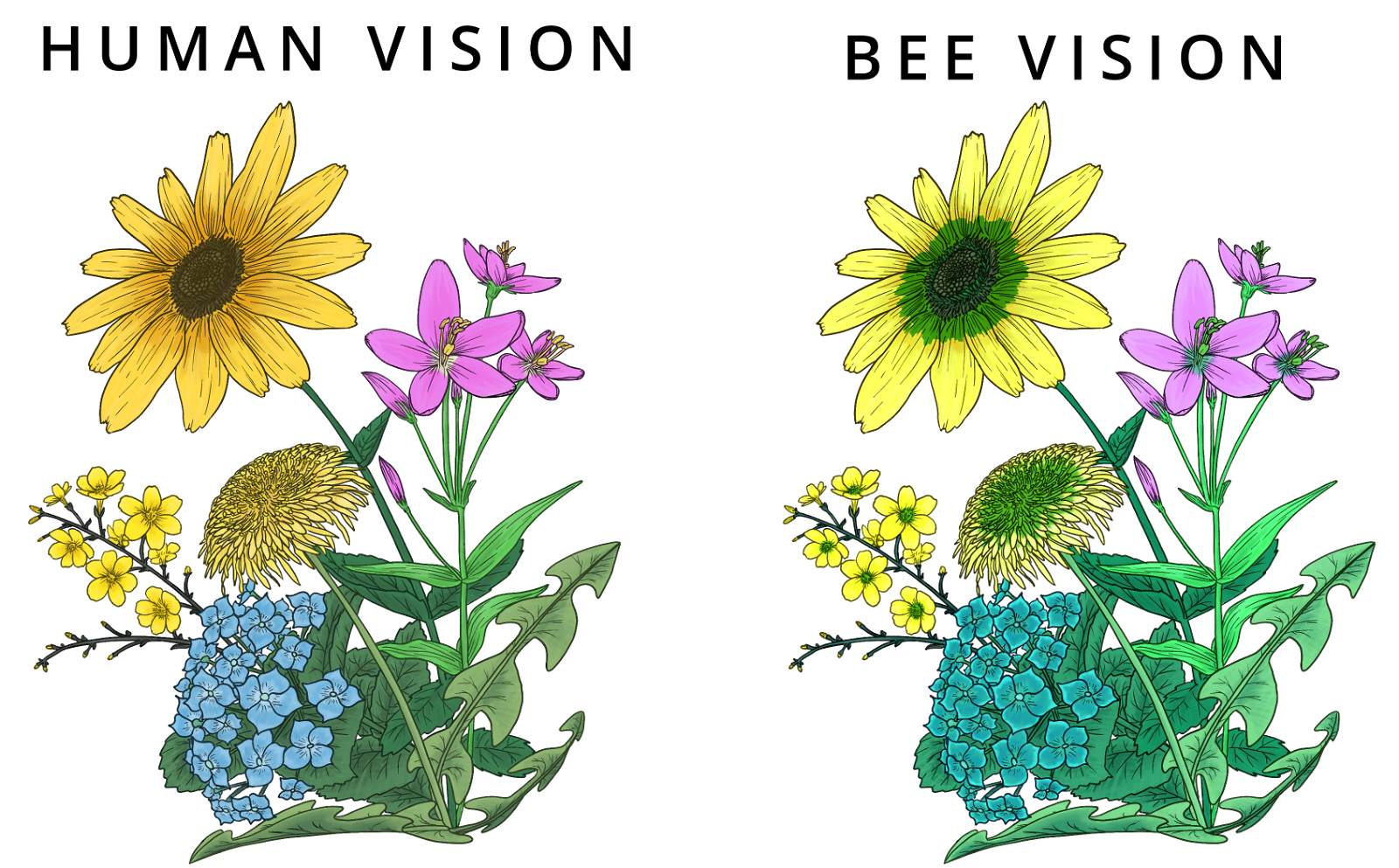
Pattern
Not seeing the nectar guides? Try looking under ultraviolet (UV) light.
Humans don't normally see UV light, but bees and butterflies do. So, what looks like a solid-color flower to humans, may actually have beautiful patterns to attract pollinators.
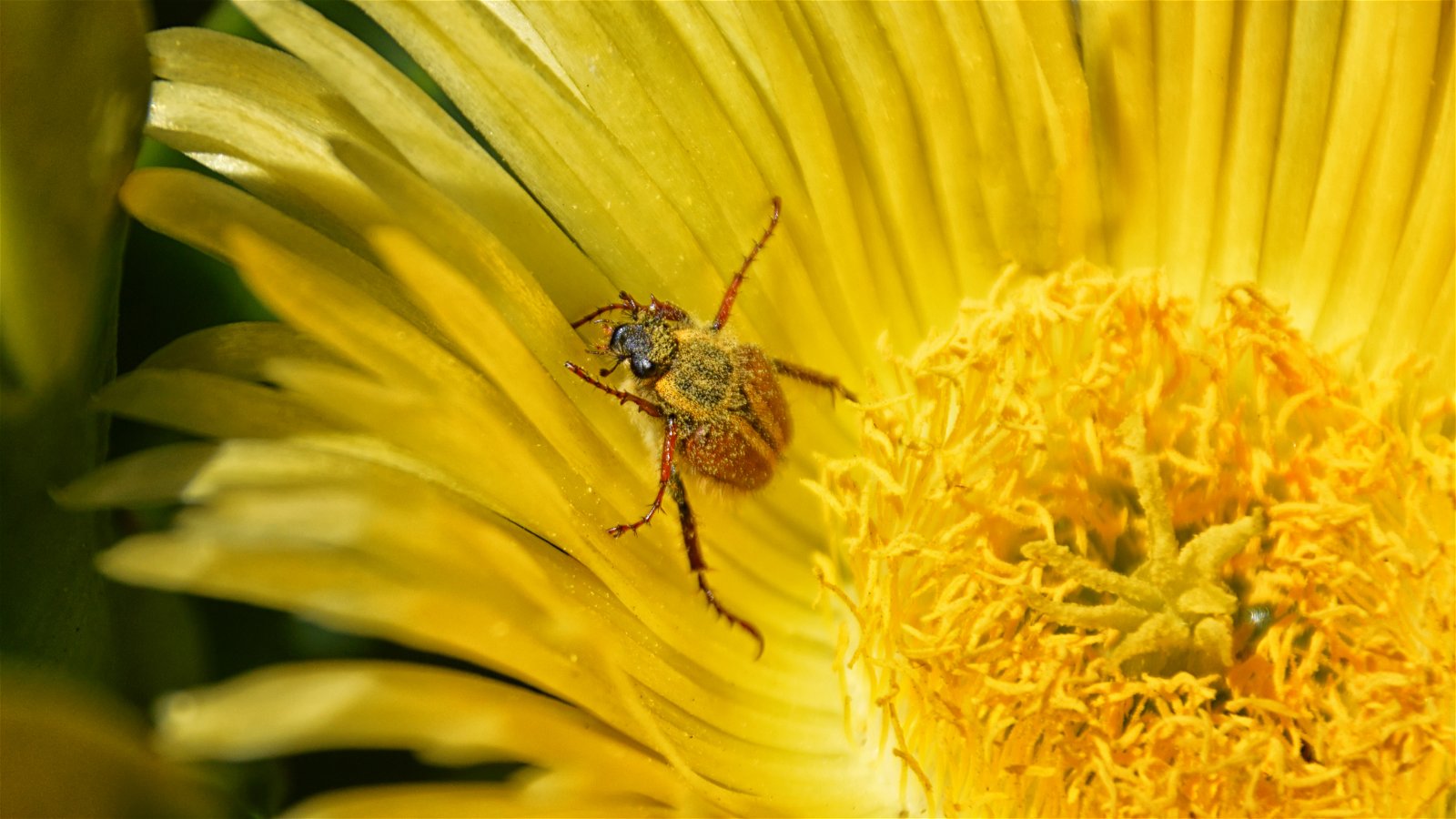

Shape
Many pollinators, like bees, butterflies, and beetles, need somewhere to land while they feed.
Beetles in particular are less skilled fliers. They're attracted to open flowers with large petals. Here, they can easily land and crawl around while they feed.
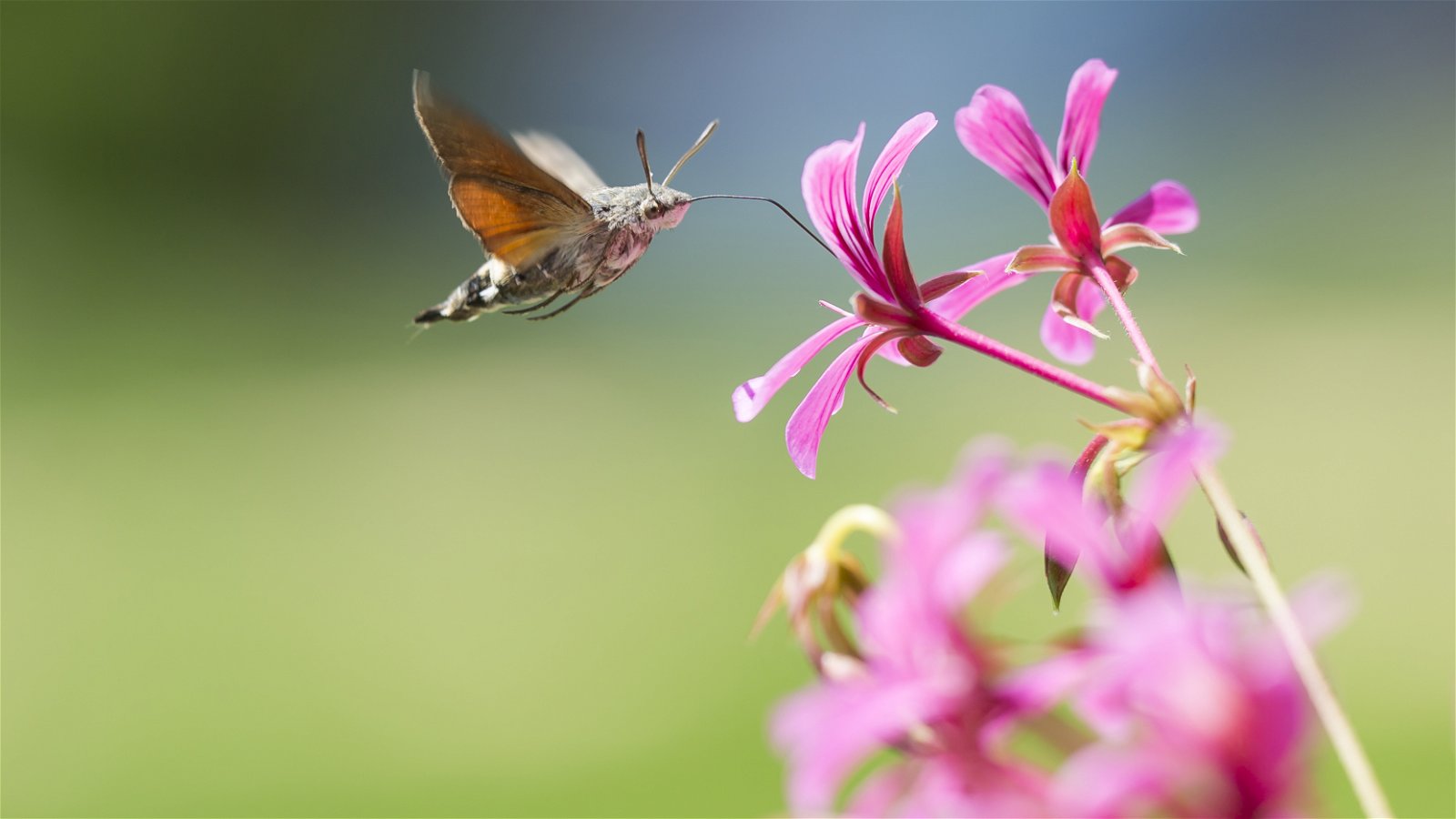

Shape
Some flowers store nectar deep within a long, tube-shaped flower. This nectar is far out of reach to a chubby, round bumblebee, but hawk moths reach it easily. The moths have a special feeding organ called a proboscis that can be up to 13 inches long!
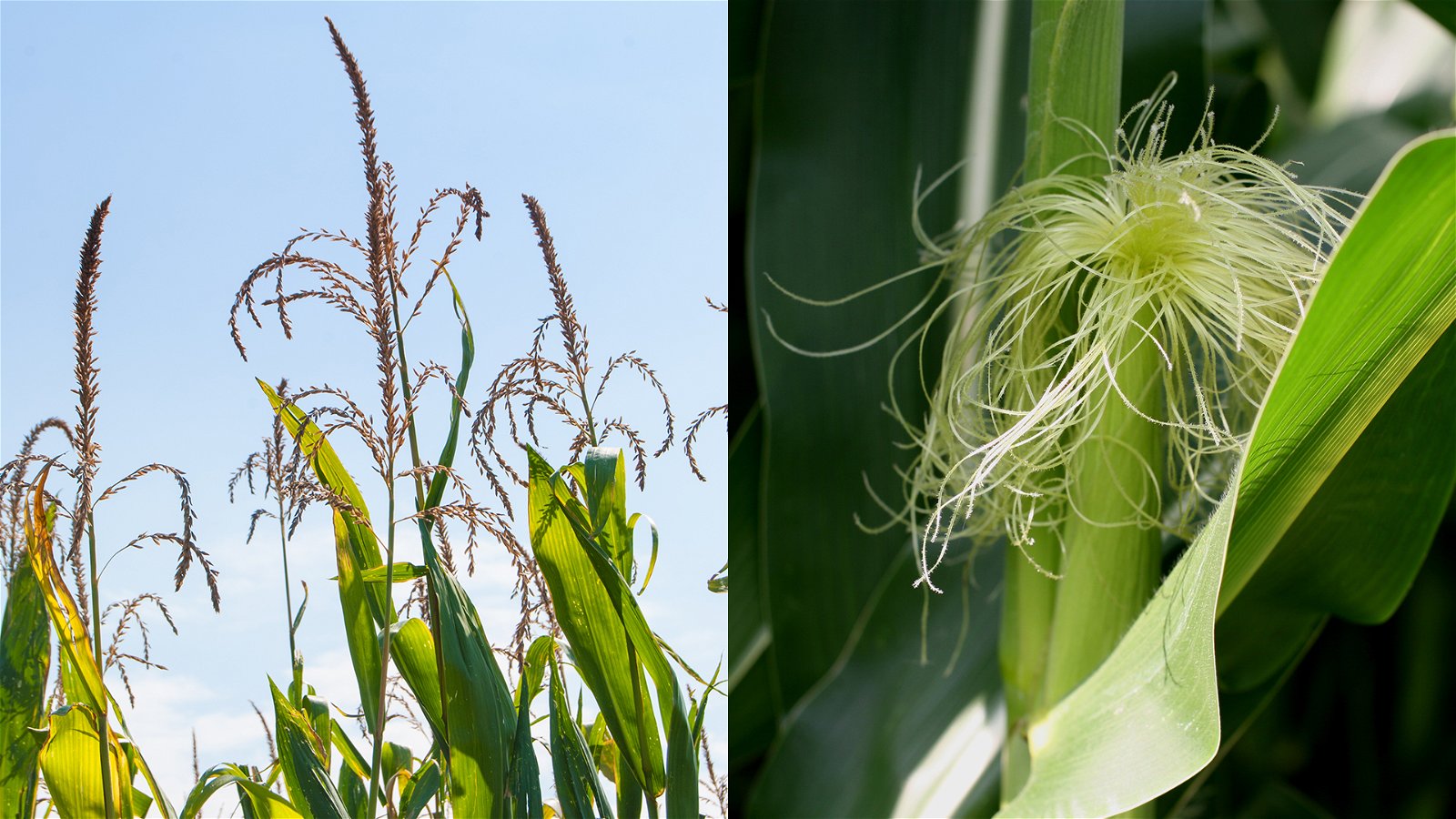

Shape
Flowers pollinated by the wind have special structures that are shaped to disperse or catch pollen.
In corn, male flowers at the top of the plant produce pollen. It is blown by the wind onto the female flowers. The female flowers have a special structure - corn silk - that catches the pollen.
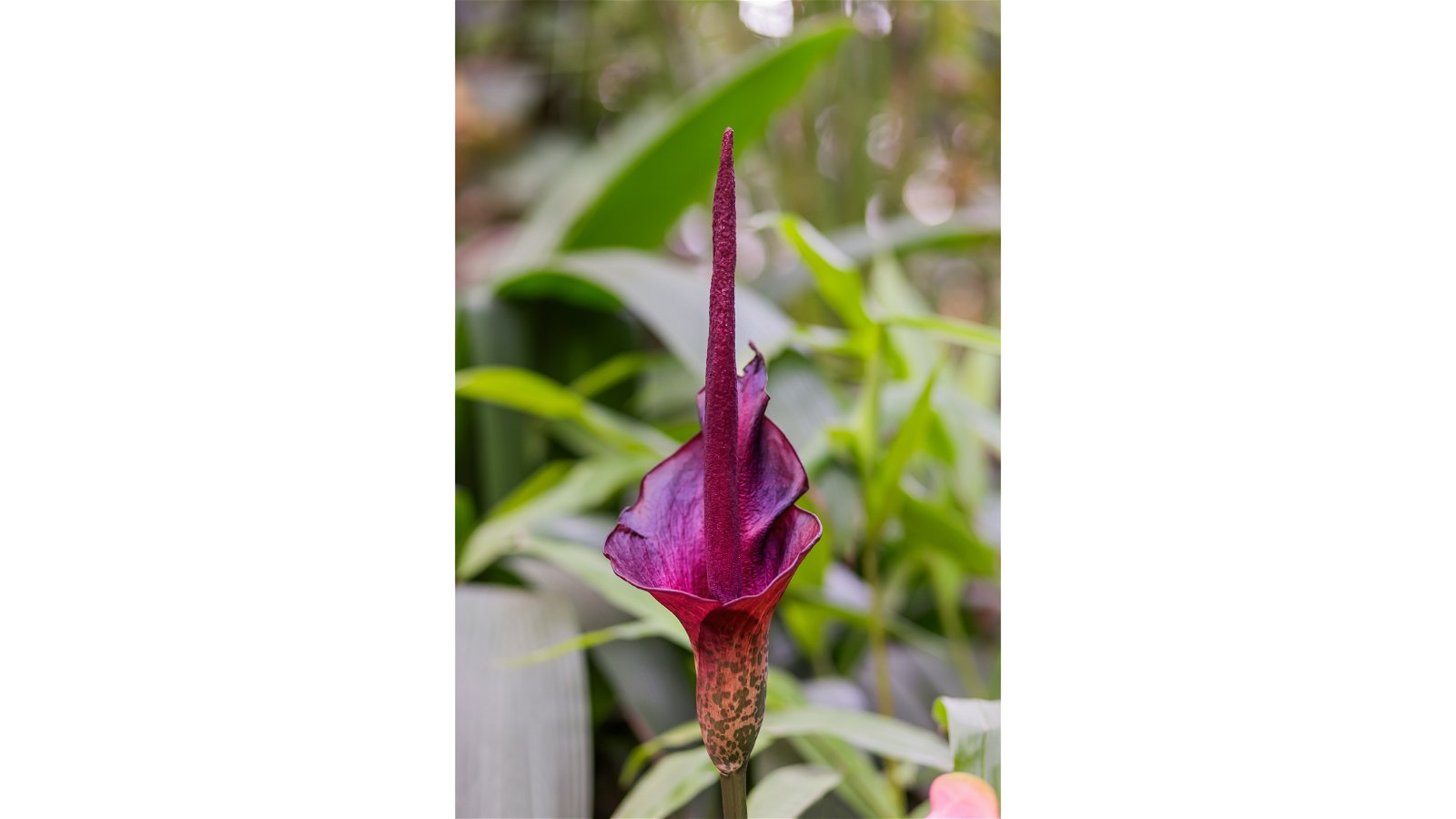

Scent
Many flowers produce fragrance to draw in pollinators.
But what smells good to a pollinator doesn't always smell good to us! Voodoo lilies have a putrid odor, often compared to rotting flesh. While humans may avoid these plants, certain flies and beetles find the scent quite enticing.
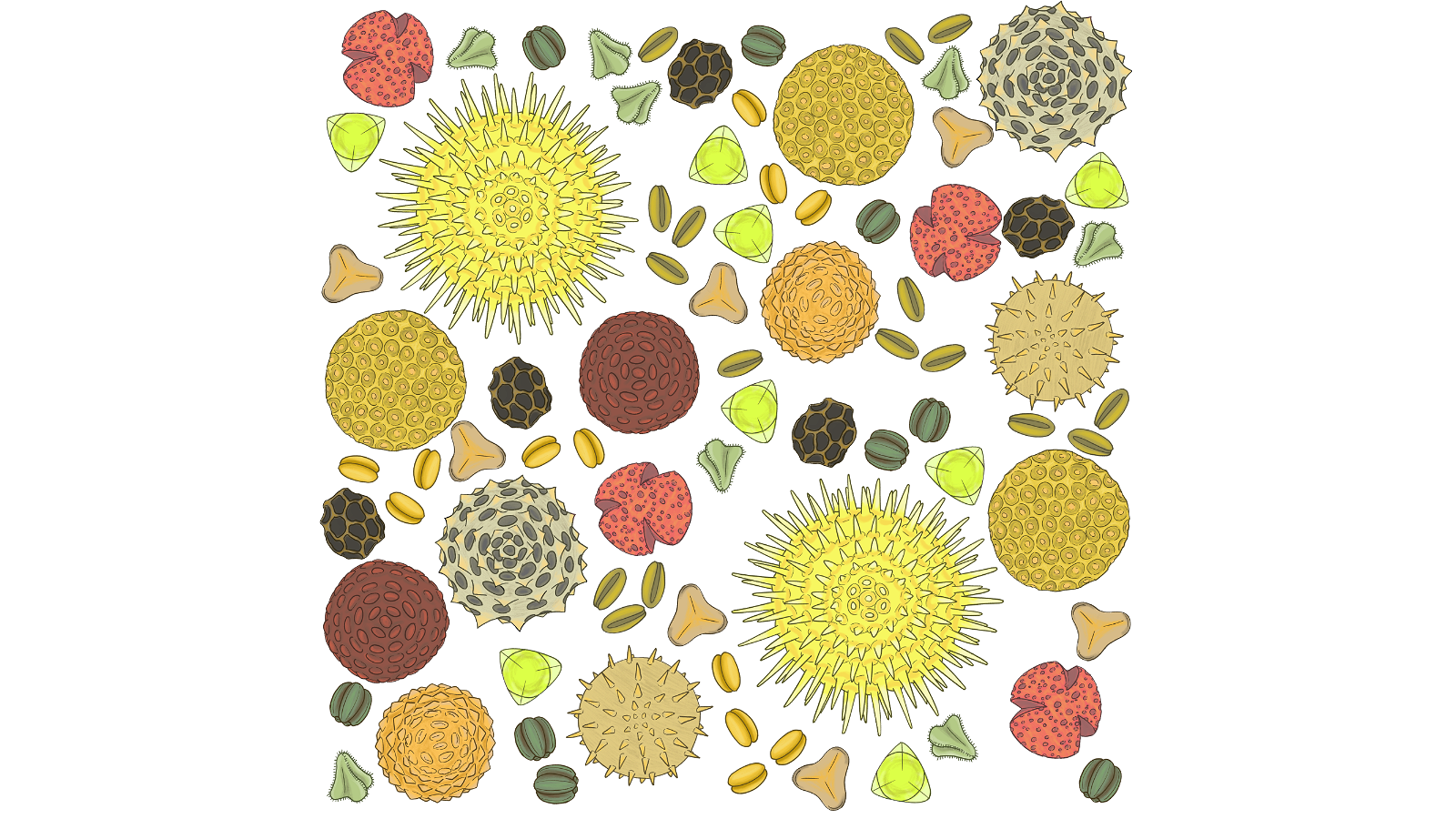

Pollen
Flowers that rely on bees, wasps, beetles, and flies for pollination make plenty of these insects' favorite food — pollen.
Pollen can look quite different between flower types. Large, sticky grains adhere to fuzzy bumblebees and are eventually left at a future flower. Small, smooth grains are more easily moved by the wind.
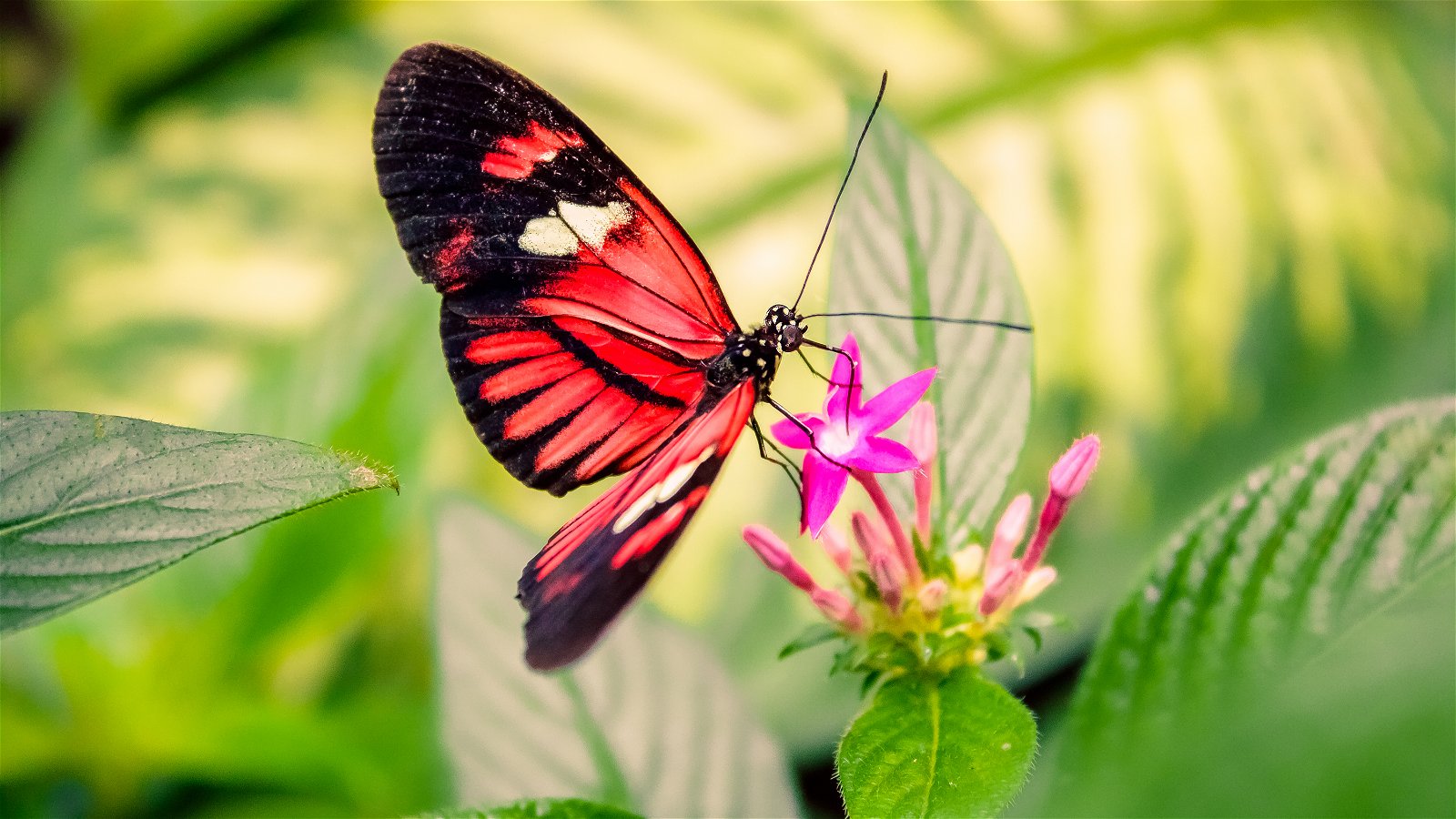

Nectar
Some pollinators prefer to eat nectar. These include bats, birds, moths, and butterflies. Often the nectar is hidden to ensure pollen gets moved around as the animals search for food.
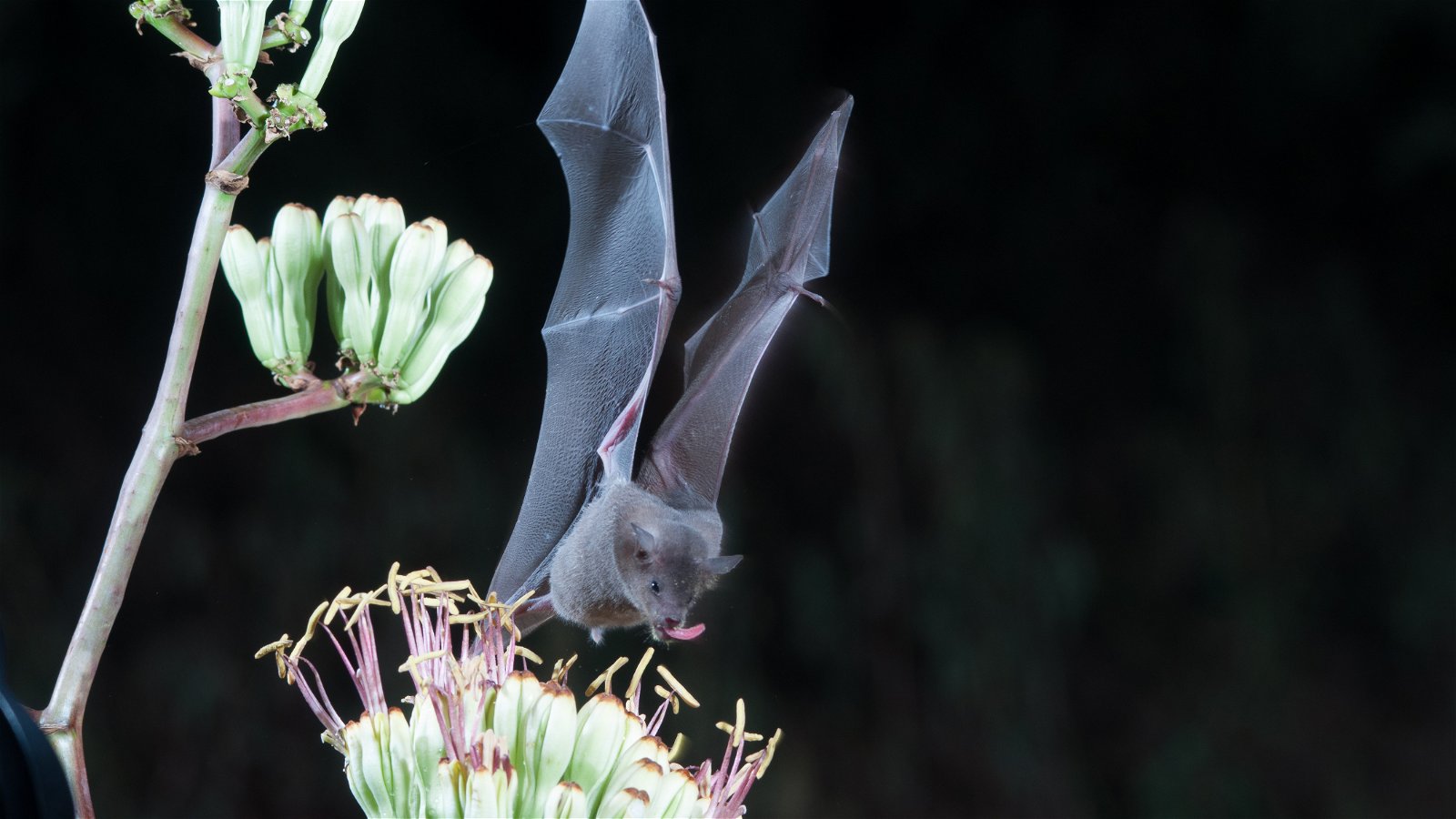

Bloom Timing
Even at night while we sleep, pollinators are hard at work. Certain flowers remain closed during the day, but open at night to attract nocturnal pollinators.
For example, night-blooming jasmine has a strong, sweet scent that attracts moths. Some species of night-blooming mangoes, bananas, agave, and cacao depend on bats.
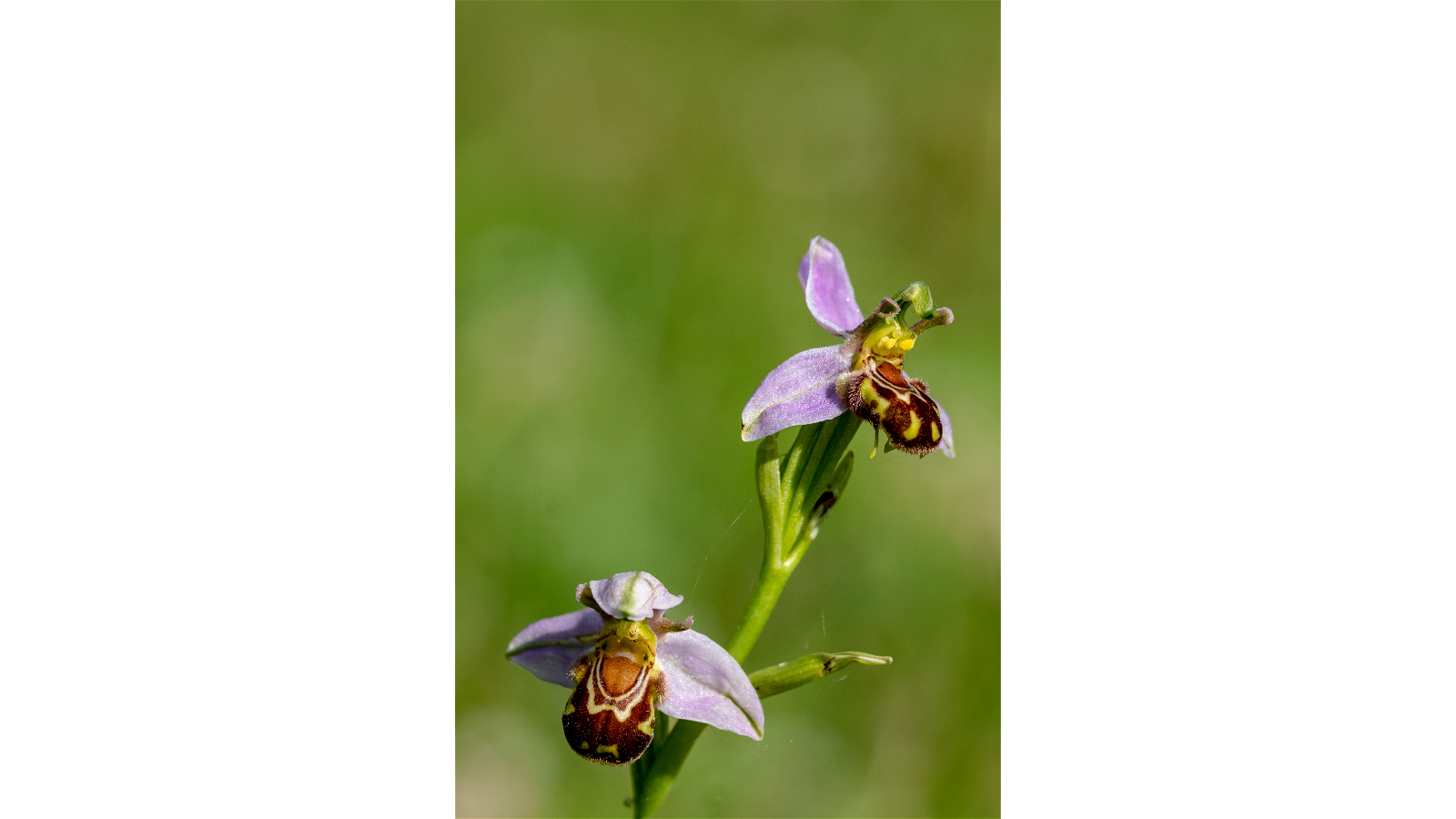

Unusual Flower Traits - Mimicry
Occasionally flowers have very unique traits that attract pollinators.
Bee orchids have brown and yellow markings that look like female bees. Male bees are drawn to the flower, thinking they've found a mate. The flower gets pollinated, but the bee is probably disappointed!
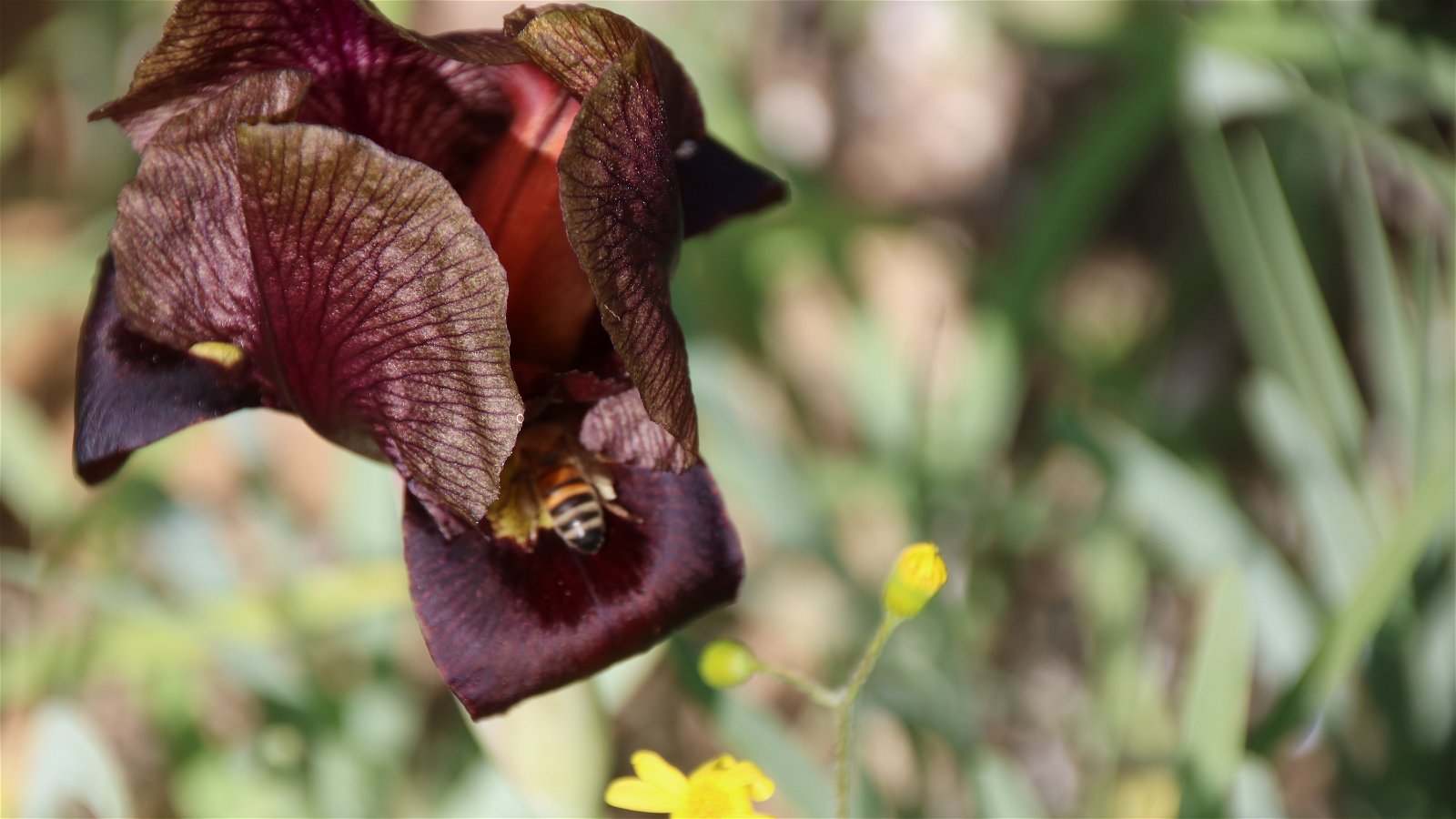

Unusual Flower Traits - Shelter
The flowers of Oncocyclus irises provide bees with a unique perk — shelter. Solitary male bees rest in the flowers overnight, transferring pollen in the process. It's thought the shape and color of the flowers warms the bees in the morning, helping them get an earlier start to their day.
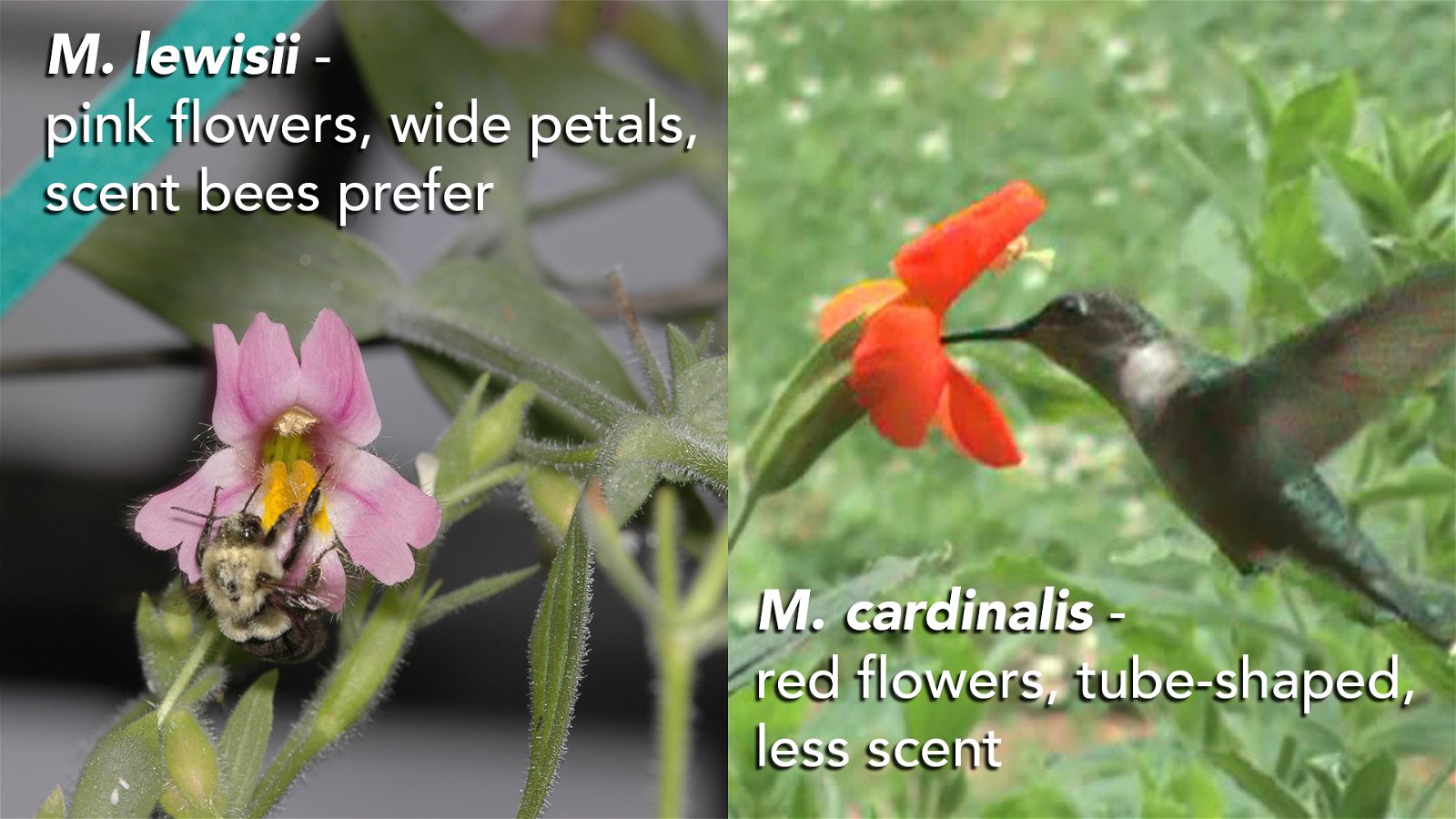
Usually, each type of flower has a set of several traits that strongly favor a certain pollinator.
For example, the monkeyflowers Mimulus lewisii and Mimulus cardinalis are closely related species. But, M. lewisii flowers have several traits that attract bumblebees, while M. cardinalis flowers have traits that strongly favor hummingbirds. Even when M. lewisii and M. cardinalis are growing near one another, pollinators visit their favorite species and usually ignore the other.